Introduction
Specimen collection is an essential stage in medical diagnostics, assuring reliable test results and efficient patient care. Proper collecting techniques are critical for avoiding contamination, preserving sample integrity, and enabling accurate laboratory analysis. This article looks at the significance, types, processes, and best practices for specimen collection.
Importance of Proper Specimen Collection
Collecting specimens correctly is essential to prevent contamination, ensure reliable test results, and facilitate accurate medical diagnoses. Errors in specimen collection can lead to misdiagnosis, delayed treatment, and even life-threatening consequences. Adhering to standardized procedures improves patient outcomes and enhances the overall efficiency of healthcare services.
Types of Specimens Collected in Healthcare
Various specimens are collected depending on the medical tests required. Below are some of the most common types:
a) Blood Samples
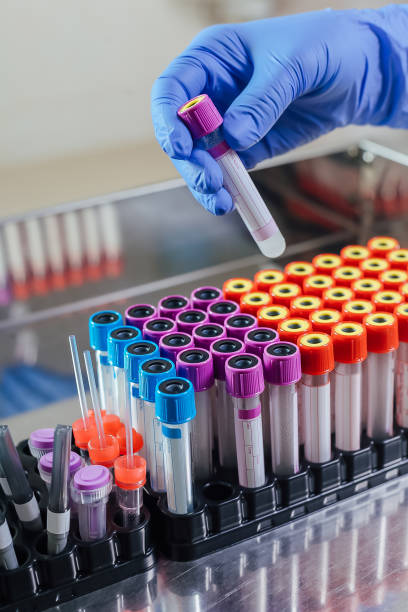
Blood specimens are commonly collected for laboratory testing to assess overall health, detect diseases, and monitor treatment effectiveness. Blood is typically drawn via venipuncture or a fingerstick, with special attention given to anticoagulation and proper tube labeling.
b) Urine Samples
Urine collection is often used to test for infections, kidney function, and metabolic disorders. Depending on the test, samples may be collected as a random, midstream, or 24-hour specimen.
c) Stool Samples
Fecal specimens help diagnose digestive disorders, infections, and occult blood presence. Proper collection involves sterile containers and prompt delivery to the laboratory to prevent sample degradation.
d) Sputum Samples
Sputum collection is crucial for diagnosing respiratory infections such as tuberculosis. Patients are typically instructed to produce a deep cough sample into a sterile container.
e) Swabs (Nasal, Throat, Wound)
Swabs are used to detect bacterial and viral infections, including COVID-19 and strep throat. Proper technique ensures sufficient sample collection without contamination.
Specimen Collection Procedures
Proper collection procedures vary by specimen type but generally include the following steps:
a) Preparing for Collection
Proper preparation, including labeling and using sterile equipment, is key to an accurate and safe collection process. Healthcare professionals must verify patient identity, explain the procedure, and use appropriate personal protective equipment (PPE).
b) Collection Techniques for Different Specimens
Different types of specimens require specific collection techniques to maintain sample integrity and prevent contamination. For example, blood draws should be performed using aseptic techniques, while urine samples must be collected in sterile containers and stored properly before analysis.
c) Handling and Transportation
Specimens must be properly stored and transported to ensure their stability and prevent degradation before analysis. This includes maintaining appropriate temperature conditions, using leak-proof containers, and documenting the collection and handling process to maintain chain of custody.
Common Challenges in Specimen Collection and How to Overcome Them
Errors such as improper labeling, contamination, or inadequate sample volume can affect diagnostic accuracy, but proper training and adherence to protocols help mitigate these risks. Healthcare professionals must be vigilant in following collection guidelines, educating patients on proper sample collection techniques, and utilizing quality control measures to ensure consistency.
Safety and Ethical Considerations
Ensuring patient comfort, following infection control measures, and maintaining confidentiality are crucial aspects of ethical specimen collection. Patients must be informed about the procedure, potential risks, and their rights regarding test results. Additionally, adherence to strict hygiene protocols minimizes the risk of infection transmission.
Conclusion
Proper specimen collection is fundamental to accurate diagnostics and quality patient care, making it an essential skill in healthcare settings. By following best practices, healthcare professionals can improve diagnostic reliability, enhance patient safety, and contribute to effective disease management.
Comments on “Specimen Collection: An Important Process in Medical Diagnostics.”